Economical heating and installation of a multi-circuit system in an apartment and in a house
How to make economical heating and installation of a multi-circuit system operating from a single heat source? This is achieved using various mixing circuits and valves, which ensure the distribution of coolant to end consumers (radiators, heated floors and other types of heating). The combination of circuits and their joint work is the basis of a modern heating system powered by one or more boilers.
Why do we focus on this? When installing an electric heating system for an apartment as a backup, when it is not possible to make economical pellet heating and convert the heating riser, you can deploy a backup water circuit powered by an economical electrode boiler. These boilers are produced in a monoblock form factor with a control unit that maintains the temperature in the radiator line. For this reason, it makes sense to install a separate low-power electric boiler for each circuit. It is compact and convenient, even with mechanical adjustment. Thus, there is no point in implementing multi-loop.
But when a large house is served from one heat source, a multi-circuit heating system is installed by default.
How many circuits to make in the heating system
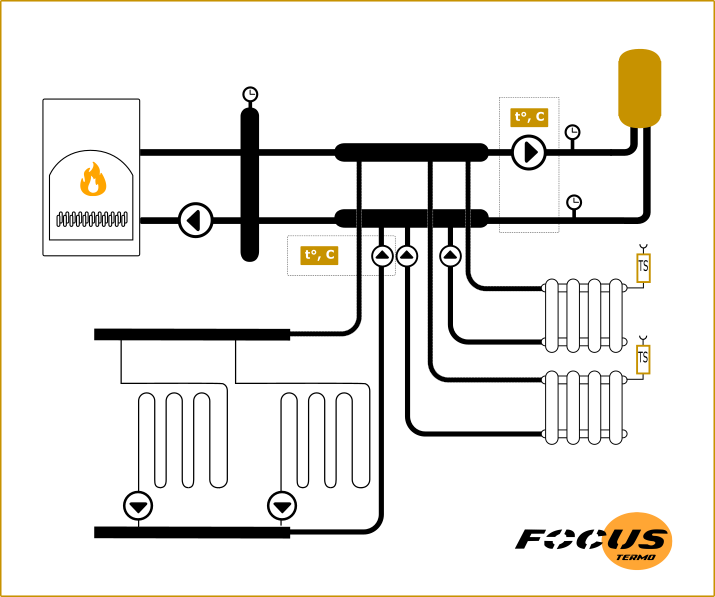
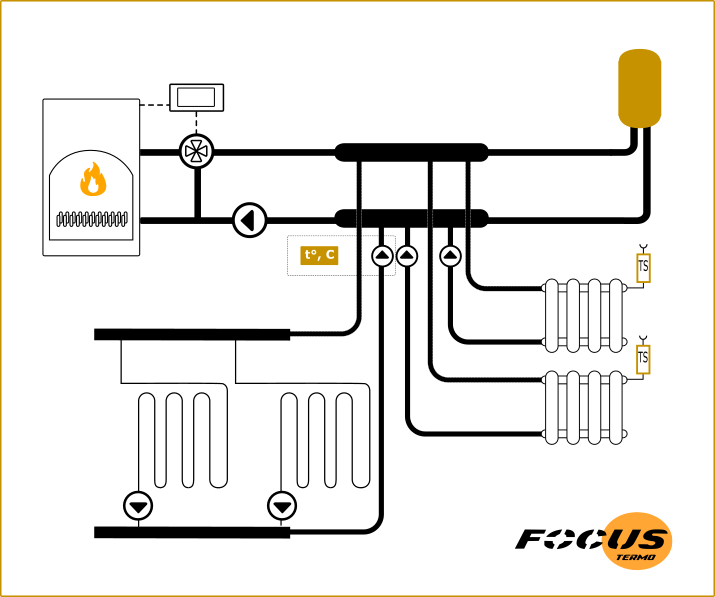
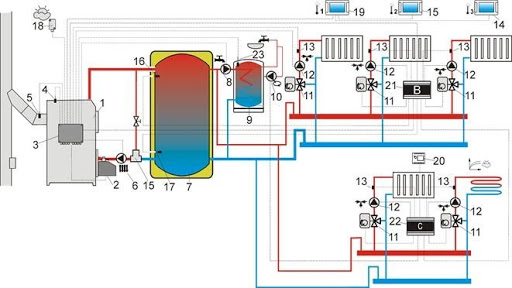
The example shows a schematic diagram of connecting a boiler to a multi-circuit system. In the first illustration, using a hydraulic arrow and collectors, in the second case, using only collectors. Manifolds for routing circuits can be installed in a small boiler room, when hydraulic switches are needed for heating systems with a large number of heating devices. First of all, to separate the boiler (heating) and boiler circuits.
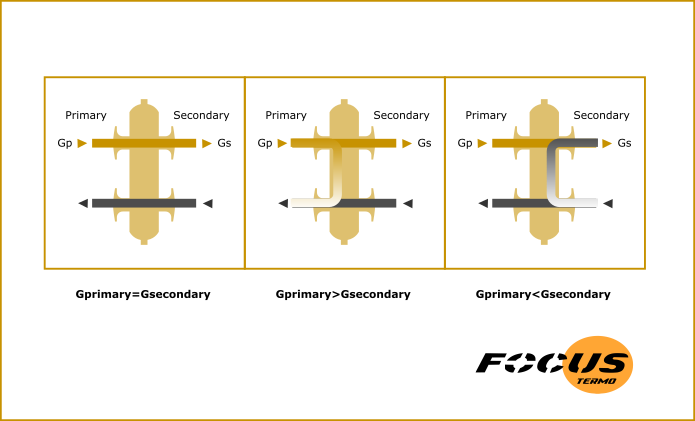
Hydraulic arrows are used in medium and high power systems and, first of all, make it possible not to balance the water flow with different circuits. They are also used in systems where several heating boilers are connected.
With a hydraulic arrow, you can safely connect as many circuits as you like, which have enough boiler power to heat them.
When the boiler circuit is connected directly to the manifold with a pump on the “return”, then in this case the boiler circuit has a strong influence on the boiler circuit. First of all, because the pumps connected to the system cannot provide the same coolant supply pressure and create parasitic flows that lead to unexpected effects. The heating system itself without a hydraulic arrow turns out to be uneconomical. Without its balancing functions, it is quite difficult to make climate control, since in zone heat flow control systems (valves) zones of system imbalance are created. Heating and installation of a multi-circuit system requires a project; a hydraulic switch can significantly reduce the thermodynamic calculations of the system.
Heating and installation of a multi-circuit system is ultimately best done in all cases where it is necessary to connect more than 3-5 radiators to the heating system, as well as additional heat consumers, such as hot water supply and heated floors.


The boiler circuit is often physically separated from the heating circuits and has a safety group and a boiler pump - boiler circuit
In professional systems, the boiler hydraulic circuit is separated from the main system by a hydraulic arrow. A security group is installed in it, which controls critical events that do not apply to boiler room devices thanks to the hydraulic arrow.
The solution for organizing the boiler and boiler circuit may be different; you can abandon the hydraulic arrow in favor of a buffer tank. This circuit is the heat source for the buffer tank, which has a dual purpose. Heating and installation of a multi-circuit system often involve a heat accumulator as a container that lowers the temperature.
On the one hand, it is a tank for discharging excess heat in case of overheating, on the other hand, it acts as a heat accumulating tank. It is usually installed in systems with solid fuel boilers, when heat for radiators is used during periods of no heating from TT boilers. At this moment, there is no need to connect backup electric heating, which provides significant savings.
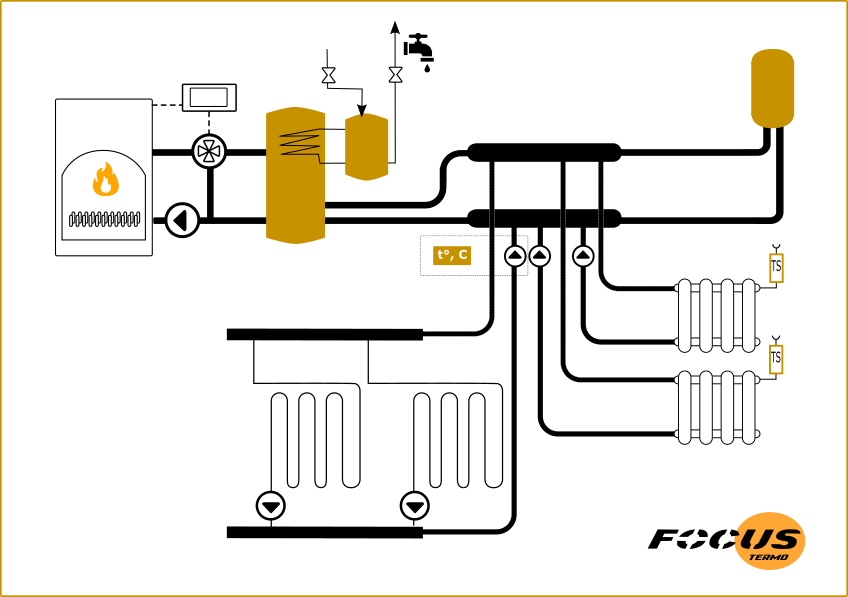
Hydroarrow as a universal mixing unit
Regardless of the presence or absence of a buffer tank in the system, the hydraulic arrow will be an effective way to separate circuits and install multi-circuit heating. This is especially effective in cases of heating large houses. Several radiator pipes and a low-temperature heating circuit with heated floors can be connected to the hydraulic arrow.
In other words, you don’t have to do heating around the perimeter of your home, but allocate separate heating lines of 3 or a maximum of 4 radiators. This is due to the fact that the last batteries in the chain will have a lower temperature. How to equalize the temperature in radiators, we wrote separately. In general, this can be done using a pump group, including one controlled via WI-FI or an Internet module.
Cast iron batteries are not a panacea
Radiators made of cast iron are a rational solution, since such batteries take the blow during abnormal operation of the TT boiler when connected directly to the circuit. In this case, the ability to regulate temperature is limited. However, you can increase system safety by installing a manual boiler controller. It will control the temperature of the coolant in the DHW circuit.
If you need to implement branching, we recommend installing a pump on the “return” circuit using a bypass. The pressure it creates will help equalize the temperature in the heating circuit.
Climate control, heating and installation of a multi-circuit system
Climate control systems are a control module that connects the operation of the heating circuit and temperature sensors. In essence, this is a logical add-on that in the simplest way controls the operation of heating pumps, valves and other final devices.
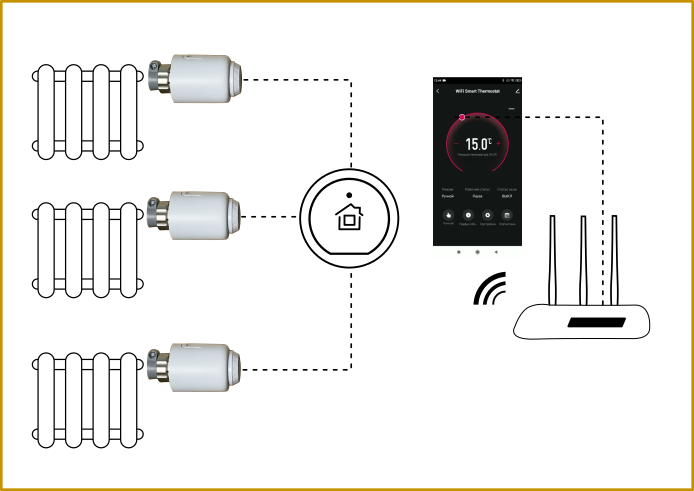
More precise adjustment is achieved if you have bimetallic radiators (with operating pressure up to 35 bar) and thermostatic valves installed, as well as an adjustable pump group on the low-temperature line of heated floors. Heating and installation of a multi-circuit system by default implies adjustment; it can be implemented using a programmer, for example, PLUM or controlled mechanically.





