Greenhouse automation based on boiler climate control
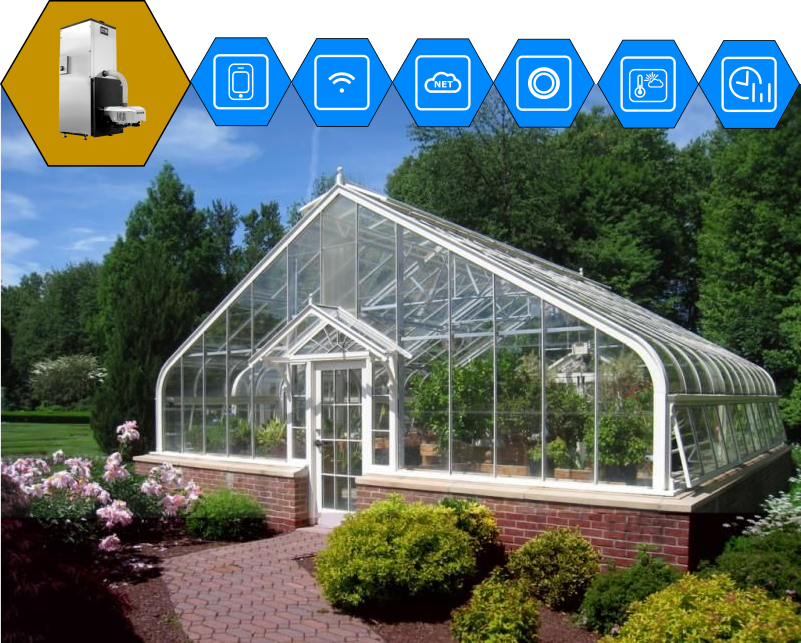
Greenhouse automation involves the use of various technologies and devices to monitor and regulate conditions within the greenhouse to optimize plant growth and development. The devices regulate climate parameters, automatic irrigation and fertilization, heating and air conditioning, lighting, monitoring and control of climate parameters, and also control the level of safety in the event of informal equipment failure.
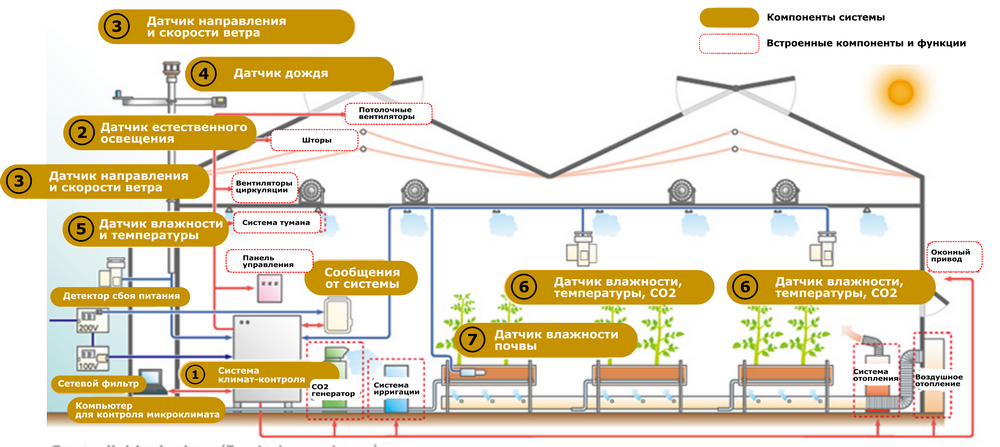
Greenhouse automation and its implementation
Sensors for temperature, humidity, light and other parameters are used to continuously monitor climate conditions inside the greenhouse. Based on the data obtained, the systems automatically control the operation of heaters, cooling systems, ventilation and humidification to maintain optimal conditions for plants.
Automated irrigation and fertilization systems allow you to accurately dose water and nutrients and distribute them to plants in the right quantities and at the right time. This increases resource efficiency and improves plant growth and development.
Greenhouses often use artificial lighting systems, especially in winter or when there is insufficient natural light. Automated lighting control systems allow you to adjust the duration and intensity of light according to the needs of the plants.
Using special software solutions and applications, you can monitor the condition of plants, collect and analyze data on growth, yield, diseases and pests, as well as remotely control greenhouse automation systems.
Some greenhouse automation systems also include safety features such as automatically shutting off electrical equipment in case of emergency or preventing overheating and waterlogging. In general, greenhouse automation can increase the productivity and efficiency of the plant growing process, reduce resource costs and improve the quality of the crop.
Zone heating control
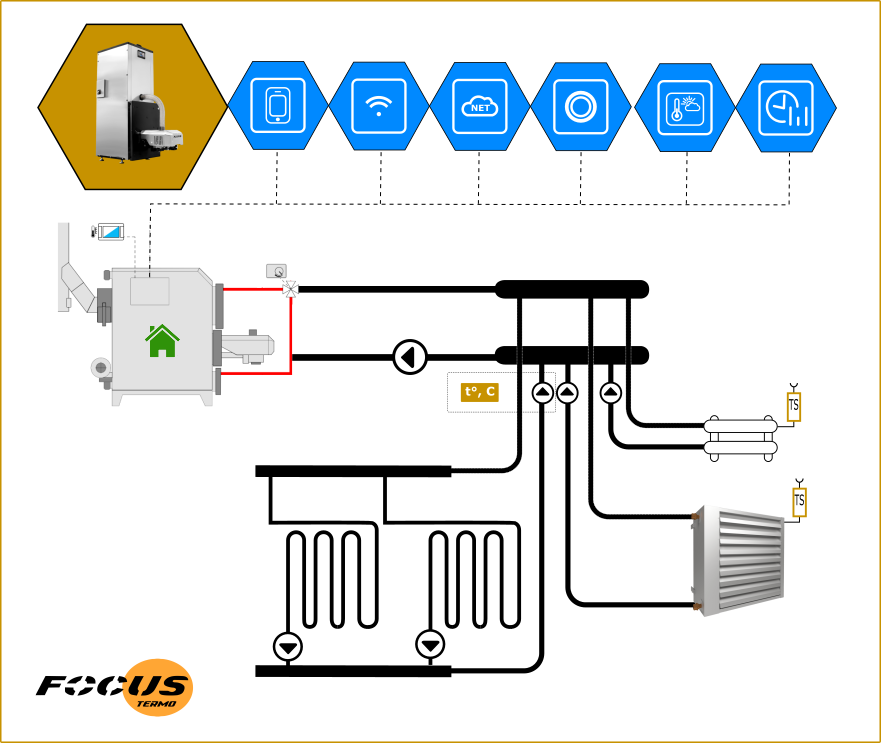
Automated greenhouse heating with zone control is a system that allows you to effectively control the temperature in different zones of the greenhouse depending on the needs of the plants and the current climate conditions.
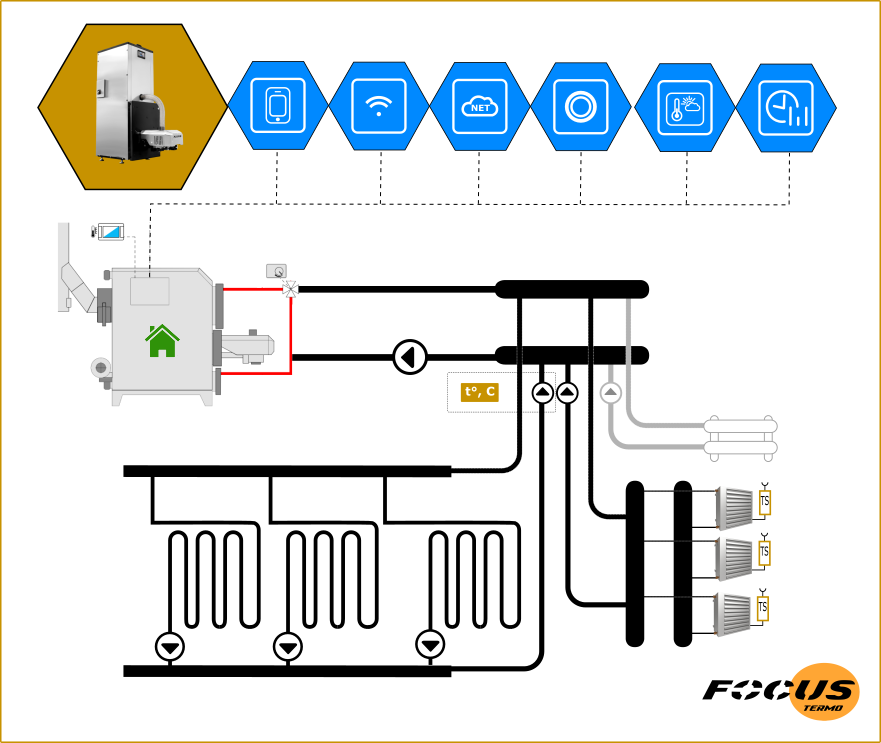
To heat a greenhouse, various heat sources can be used, including stoves or solid fuel boilers (for example, pellets). This approach implies autonomy, but depending on the type of boiler different levels of automation. The final heat sources for heating, implemented in the form of heating circuits, can be located around the perimeter or distributed over different zones of the greenhouse.
To ensure zonal heat regulation in the greenhouse, various heat distribution systems are used, such as underfloor heating, radiators, fan heaters or infrared heaters as additional heating.
Temperature sensors are located in different areas of the greenhouse and transmit information about current temperature conditions to the controller. Based on this data, controllers control the operation of heat sources and heat distribution systems to maintain optimal temperature conditions in each automation zone of the greenhouse.
To configure and control the heating system and zone regulation, special software or control interfaces are used, which allow you to set the desired temperature parameters for each zone, create operating schedules and monitor the status of the system. Greenhouse automation as a task is perceived and implemented more widely.
Automated heating with zone control allows you to optimize energy and resource consumption, since heating can be directed only to those zones where it is really needed, which reduces energy costs and increases the energy efficiency of the entire heating system.
Combination of heating with solar system
Typically, a formula is used to estimate the energy consumption for heating a greenhouse, taking into account greenhouse area, insulation, climate conditions, and desired temperature. The exact number of kilowatts of power required can be calculated by an engineer based on your greenhouse's specific conditions and heating requirements, but the default costs will be high. For this reason, natural heat sources are also used.
The heating system in a greenhouse can be integrated with a solar system to optimize the use of solar energy and increase energy efficiency. It is also possible to install a fire tube heat exchanger, which will heat a bulk stone heat accumulator under the soil of the greenhouse. This will reduce heating costs.
Solar collectors can be installed on the roof or on special structures in the greenhouse to collect solar energy. This energy can then be used to heat the heating medium that circulates through the greenhouse heating system.
Solar energy can be used to heat thermal storage devices, such as ground thermal batteries, which can store excess heat and release it to the heating system during times of solar energy shortage or at night. Greenhouse automation will help control the parameters of the hybrid system.
It is possible to create a combination system that uses both solar energy and other energy sources to provide the proper level of heating in the greenhouse. This allows solar energy to be used as an additional or primary heat source, depending on conditions. Integrating a heating system based on a solid fuel boiler with a solar system allows you to reduce energy costs and make the heating process more environmentally friendly and sustainable.
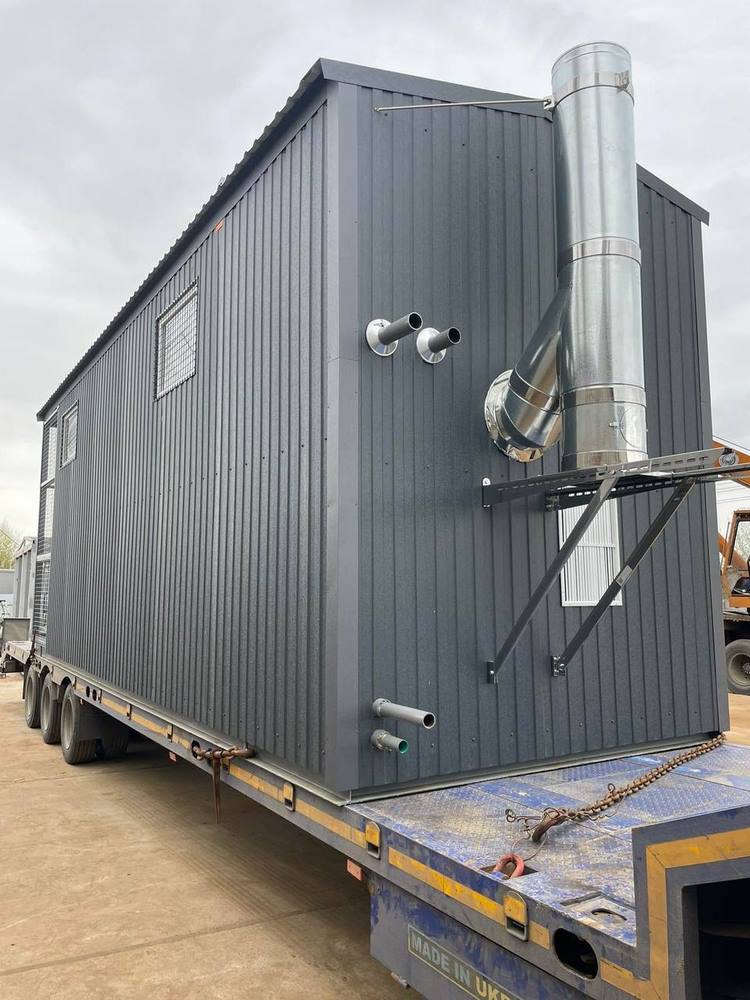
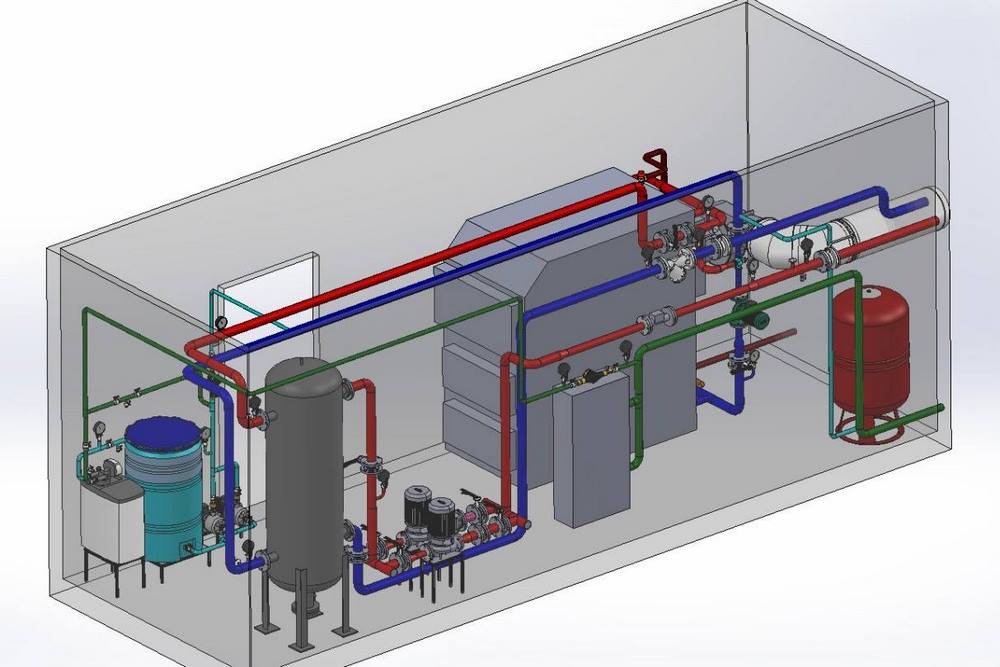
Modular boiler rooms for greenhouses
You can purchase modular boiler rooms FOCUS for heating greenhouses. This is a complete solution that does not require design or construction work. The units are supplied in stationary form and on a mobile chassis, so you can use the modular boiler room as needed and transport it to the desired location. It looks like an agricultural outbuilding.